Search Result
Results for "
50S subunit
" in MedChemExpress (MCE) Product Catalog:
9
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Target |
Research Areas |
Chemical Structure |
-
- HY-106597A
-
|
RU 38882 hydrochloride; RU 882 hydrochloride
|
Bacterial
Antibiotic
|
Infection
|
|
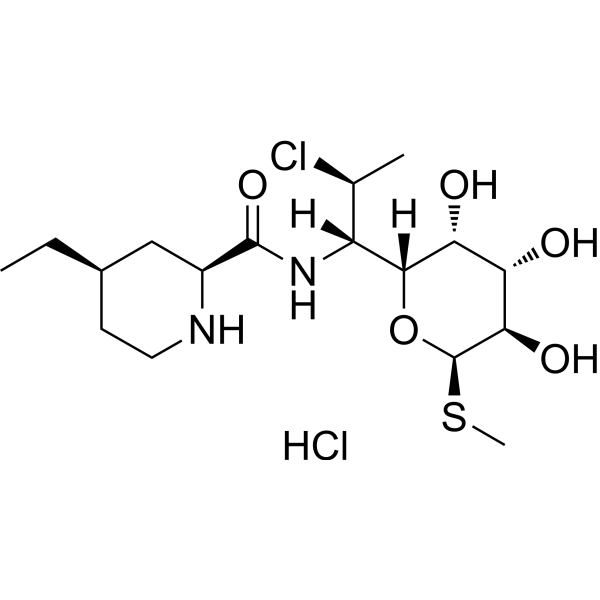
Pirlimycin (RU 38882) hydrochloride, a lincosamide antibiotic, is active against Gram-positive bacteria. Pirlimycin hydrochloride acts by inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis via binding with the 50S subunit of the ribosome .
|
-
-
- HY-N2301
-
|
Drosophilin B; Mutilin 14-glycolate
|
Bacterial
Antibiotic
|
Infection
|
|
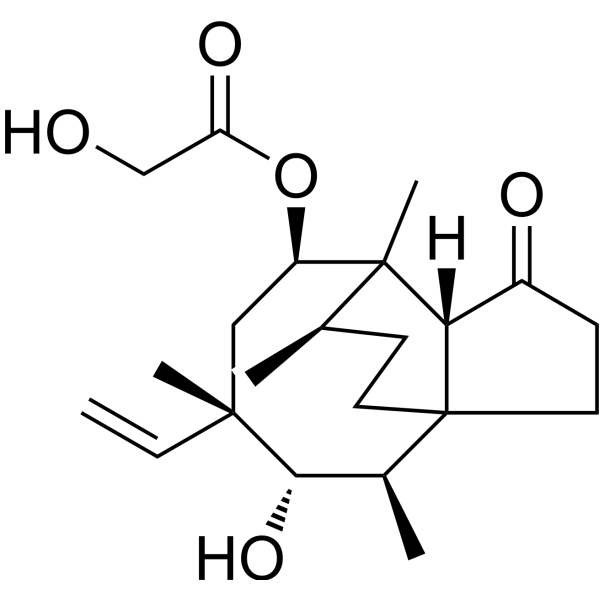
Pleuromutilin (Drosophilin B) inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit of bacteria.
|
-
-
- HY-B0027
-
|
|
Bacterial
Antibiotic
|
Others
|
|
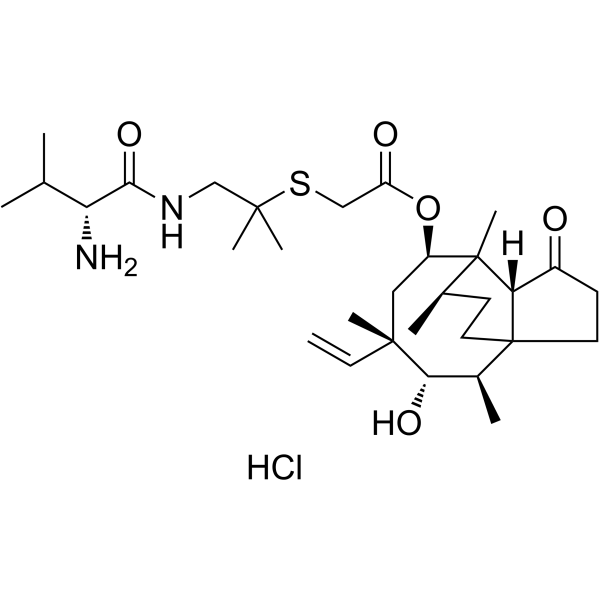
Valnemulin hydrochloride is a pleuromutilin antibiotic which inhibits protein synthesis in bacteria by binding the peptidyl transferase enzyme in the 50s ribosomal subunit.
|
-
-
- HY-14855
-
|
TR 700; Torezolid; DA-7157
|
Bacterial
Antibiotic
|
Infection
|
|
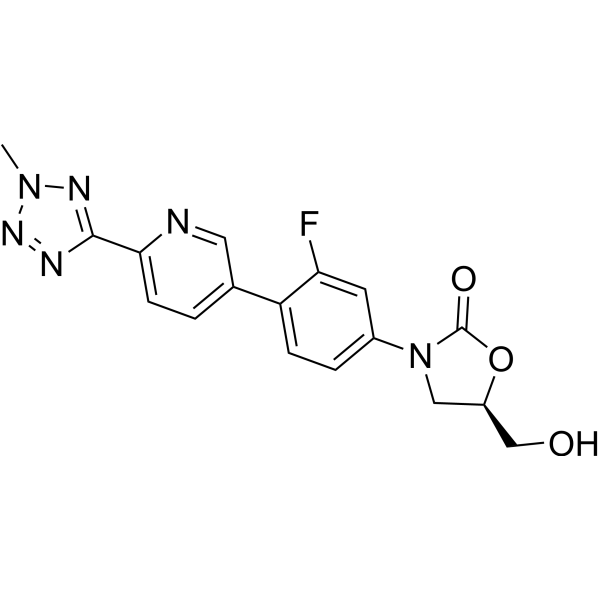
Tedizolid (TR 700; Torezolid; DA-7157) is a novel oxazolidinone, acting through inhibition of bacterial protein synthesis by binding to 23S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) of the 50S subunit of the ribosome.
|
-
-
- HY-106597
-
|
RU 38882; RU 882
|
Antibiotic
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
Pirlimycin (RU 38882), a lincosamide antibiotic, is active against Gram-positive bacteria. Pirlimycin acts by inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis via binding with the 50S subunit of the ribosome .
|
-
-
- HY-B0027R
-
|
|
Bacterial
Antibiotic
|
Others
|
|
Valnemulin (hydrochloride) (Standard) is the analytical standard of Valnemulin (hydrochloride). This product is intended for research and analytical applications. Valnemulin hydrochloride is a pleuromutilin antibiotic which inhibits protein synthesis in bacteria by binding the peptidyl transferase enzyme in the 50s ribosomal subunit.
|
-
-
- HY-B1864B
-
|
Ksg hydrochloride hydrate
|
Bacterial
Antibiotic
|
Infection
|
|
Kasugamycin hydrochloride hydrate (Ksg hydrochloride hydrate) is an antibiotic which binds both the 30S and 70S ribosome but not isolated 50S subunits. Kasugamycin hydrochloride hydrate (Ksg hydrochloride hydrate) mimics mRNA nucleotides to destabilize tRNA binding and inhibit canonical translation initiation .
|
-
-
- HY-B1864A
-
|
Ksg hydrochloride
|
Bacterial
Antibiotic
|
Infection
|
|
Kasugamycin hydrochloride (Ksg hydrochloride) is an antibiotic which binds both the 30S and 70S ribosome but not isolated 50S subunits. Kasugamycin hydrochloride (Ksg hydrochloride) mimics mRNA nucleotides to destabilize tRNA binding and inhibit canonical translation initiation .
|
-
-
- HY-B1228
-
|
Vistamycin sulfate
|
Bacterial
Antibiotic
PDI
|
Infection
|
|
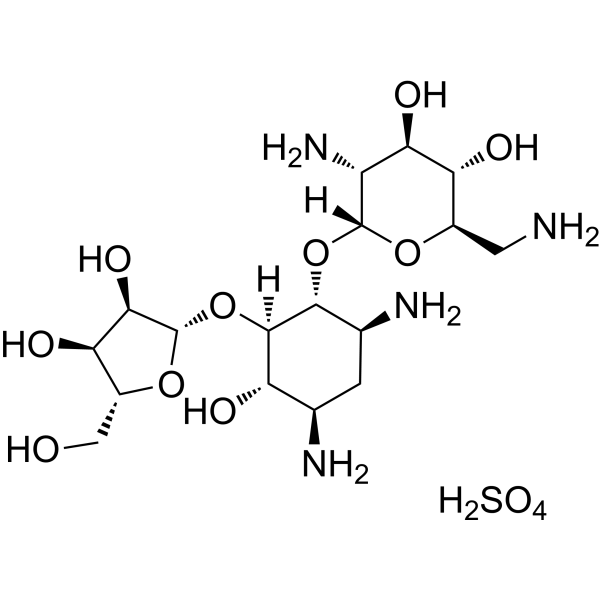
Ribostamycin sulfate (Vistamycin sulfate) is a broad-spectrum antimicrobial, inhibits bacterial protein synthesis at the level of 30S and 50S ribosomal subunit binding, also inhibits the chaperone activity of protein disulfide isomerase (PDI), used in pharmacokinetic and nephrotoxicity studies
|
-
-
- HY-B0479
-
|
Thiophenicol; Dextrosulphenidol
|
Beta-lactamase
Bacterial
Antibiotic
|
Infection
|
|
Thiamphenicol (Thiophenicol), a methyl-sulfonyl derivative of Chloramphenicol, is a broad-spectrum antimicrobial antibiotic. Thiamphenicol acts by binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit, leading to inhibition of protein synthesis and bacteriostatic effect (against Gram-negative, Gram-positive aerobic and anaerobic bacteria) .
|
-
-
- HY-118099
-
|
|
Bacterial
Drug Metabolite
|
Infection
|
|
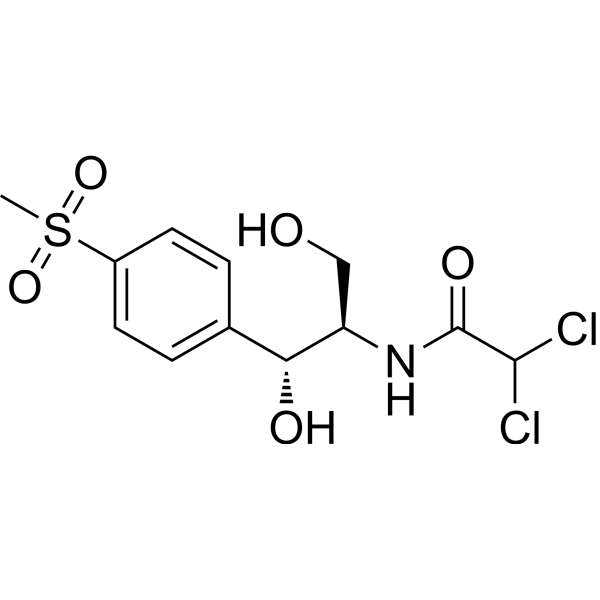
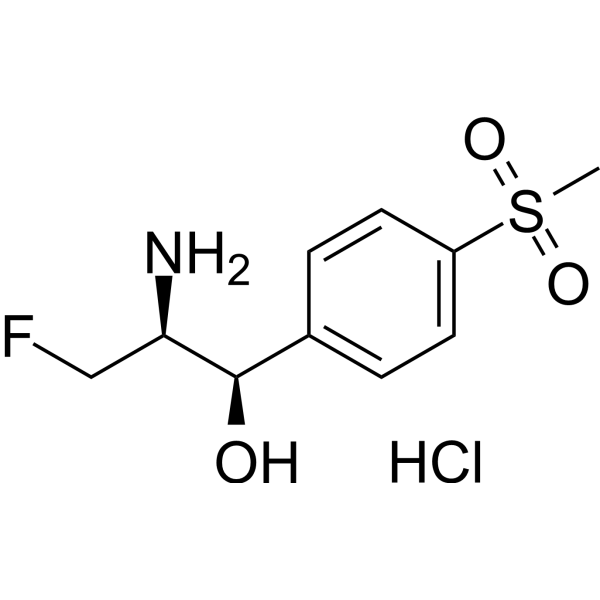
Florfenicol amine hydrochloride is a metabolite of Florfenicol (HY-B1374). Florfenicol inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by binding to 50S and 70S subunits in the ribosome to abolish the activity of peptidyltransferase. Florfenicol, is a veterinary antibiotic, can be used in aquaculture to control susceptible bacterial diseases .
|
-
-
- HY-14855S
-
|
TR 700-13C,d3; Torezolid-13C,d3; DA-7157-13C,d3
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
Bacterial
Antibiotic
|
Infection
|
|
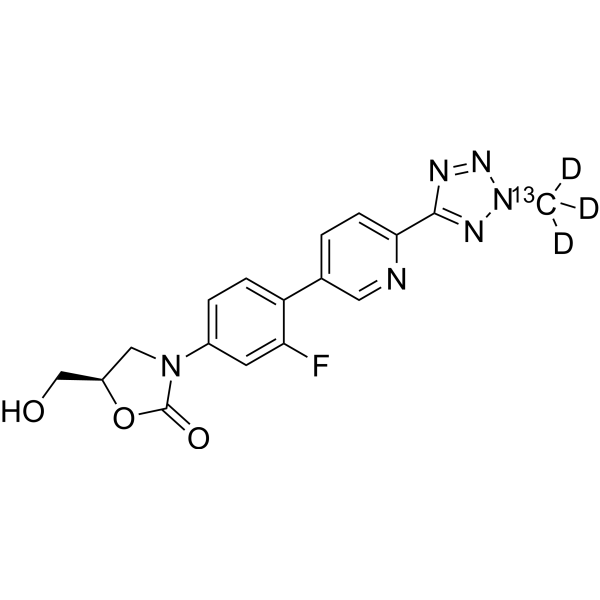
Tedizolid- 13C,d3 is the 13C- and deuterium labeled Tedizolid. Tedizolid (TR 700; Torezolid; DA-7157) is a novel oxazolidinone, acting through inhibition of bacterial protein synthesis by binding to 23S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) of the 50S subunit of the ribosome.
|
-
-
- HY-17593
-
|
CEM-101; OP-1068
|
Bacterial
Antibiotic
|
Infection
|
|
Solithromycin (CEM-101) is an orally bioavailable, effective antimicrobial agent, with IC50s for inhibition of cell viability, protein synthesis, and growth rate are 7.5 ng/mL, 40 ng/mL, and 125 ng/mL for Streptococcus pneumonia, Staphylococcus aureus, and Haemophilus influenzae, respectively. Solithromycin binds to the large 50S subunit of the ribosome and inhibits protein biosynthesis .
|
-
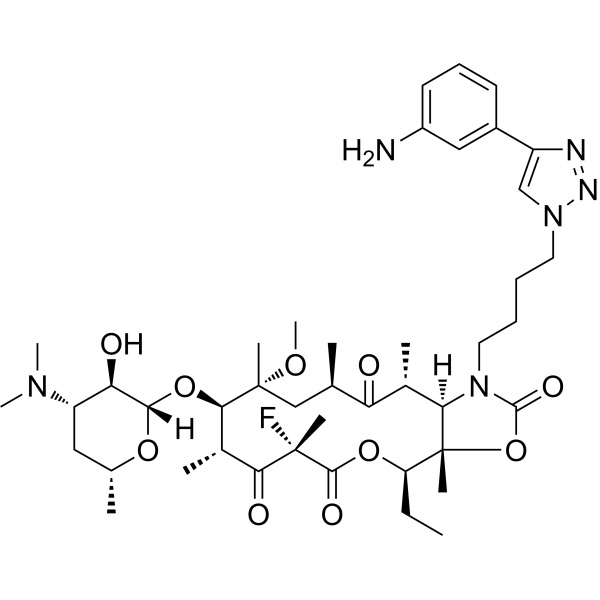
-
- HY-B0239S3
-
|
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
Bacterial
Antibiotic
|
Infection
|
|
Chloramphenicol-d4 is deuterium labeled Chloramphenicol. Chloramphenicol, a broad-spectrum antibiotic, acts as a potent inhibitor of bacterial protein biosynthesis[1][2]. Chloramphenicol acts primarily on the 50S subunit of bacterial 70S rihosomes and inhibits peptide bond formation by suppressing peptidyl transferase activity[3].
|
-
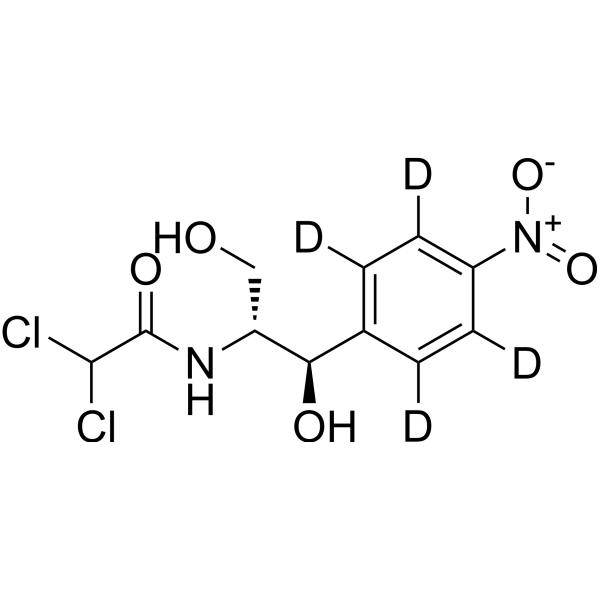
-
- HY-B0479S
-
|
Thiophenicol-d3; Dextrosulphenidol-d3
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
Bacterial
Antibiotic
|
Infection
|
|
Thiamphenicol-d3 is a deuterium labeled Thiamphenicol. Thiamphenicol, a methyl-sulfonyl derivative of Chloramphenicol, is a broad-spectrum antimicrobial antibiotic. Thiamphenicol acts by binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit, leading to inhibition of protein synthesis and bacteriostatic effect (against Gram-negative, Gram-positive aerobic and anaerobic bacteria)[1][2].
|
-
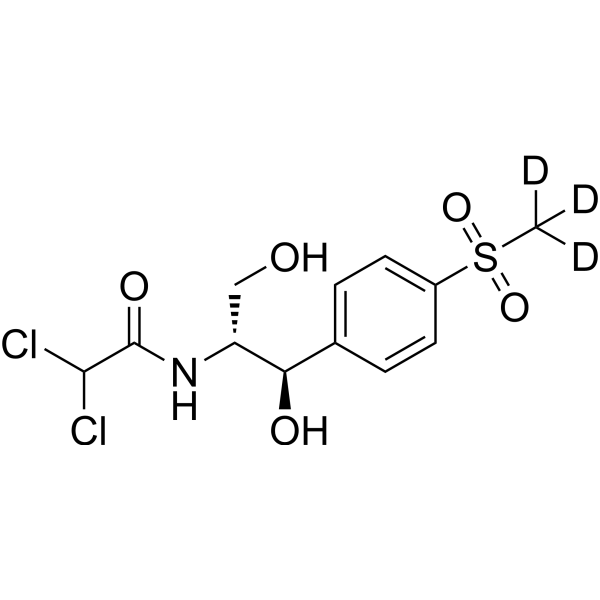
-
- HY-B0220S
-
|
|
Bacterial
Antibiotic
|
Infection
|
|
Erythromycin-d6 is the deuterium labeled Erythromycin. Erythromycin is a macrolide antibiotic produced by actinomycete Streptomyces erythreus with a broad spectrum of antimicrobial activity. Erythromycin acts by binding to bacterial 50S ribosomal subunits and inhibits RNA-dependent protein synthesis by blockage of transpeptidation and/or translocation reactions, without affecting synthesis of nucleic acid[1].
|
-
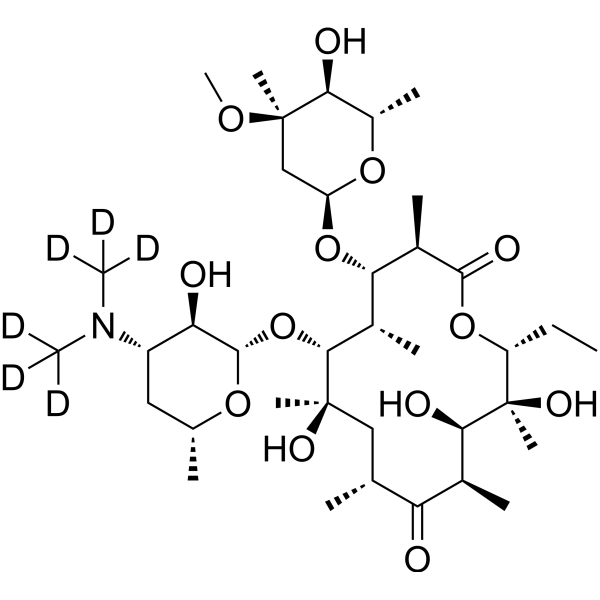
-
- HY-B0479R
-
|
Thiophenicol (Standard); Dextrosulphenidol (Standard)
|
Beta-lactamase
Bacterial
Antibiotic
|
Infection
|
|
Thiamphenicol (Standard) is the analytical standard of Thiamphenicol. This product is intended for research and analytical applications. Thiamphenicol (Thiophenicol), a methyl-sulfonyl derivative of Chloramphenicol, is a broad-spectrum antimicrobial antibiotic. Thiamphenicol acts by binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit, leading to inhibition of protein synthesis and bacteriostatic effect (against Gram-negative, Gram-positive aerobic and anaerobic bacteria) .
|
-
-
- HY-B0220
-
Erythromycin
Maximum Cited Publications
17 Publications Verification
|
Bacterial
Antibiotic
DNA/RNA Synthesis
|
Infection
Cancer
|
|
Erythromycin is a macrolide antibiotic produced by actinomycete Streptomyces erythreus with a broad spectrum of antimicrobial activity. Erythromycin binds to bacterial 50S ribosomal subunits and inhibits RNA-dependent protein synthesis by blockage of transpeptidation and/or translocation reactions, without affecting synthesis of nucleic acid [1][2]. Erythromycin also exhibits antitumor and neuroprotective effect in different fields of research [3][4].
|
-
-
- HY-B0509
-
|
BAY 41-6551 hydrate
|
Bacterial
Antibiotic
|
Infection
Cancer
|
|
Amikacin hydrate (BAY 41-6551 hydrate) is an aminoglycoside antibiotic and a semisynthetic analog of kanamycin. Amikacin hydrate is bactericidal, acting directly on the 30S and 50S bacerial ribosomal subunits to inhibit protein synthesis. Amikacin hydrate is very active against most Gram-negative bacteria including gentamicin- and tobramycin-resistant strains. Amikacin hydrate also inhibits the infections caused by susceptible Nocardia and nontuberculous mycobacteria .
|
-
-
- HY-B0220S1
-
|
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
Bacterial
Antibiotic
|
Infection
|
|
Erythromycin- 13C,d3 is the 13C- and deuterium labeled Erythromycin. Erythromycin is a macrolide antibiotic produced by actinomycete Streptomyces erythreus with a broad spectrum of antimicrobial activity. Erythromycin acts by binding to bacterial 50S ribosomal subunits and inhibits RNA-dependent protein synthesis by blockage of transpeptidation and/or translocation reactions, without affecting synthesis of nucleic acid[1].
|
-
-
- HY-B0220D
-
|
|
Bacterial
Antibiotic
DNA/RNA Synthesis
|
Infection
Cancer
|
|
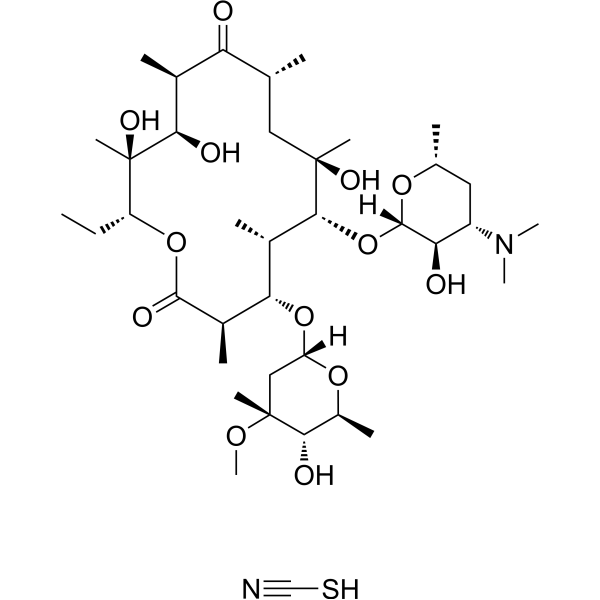
Erythromycin thiocyanate is a macrolide antibiotic produced by actinomycete Streptomyces erythreus with a broad spectrum of antimicrobial activity. Erythromycin thiocyanate binds to bacterial 50S ribosomal subunits and inhibits RNA-dependent protein synthesis by blockage of transpeptidation and/or translocation reactions, without affecting synthesis of nucleic acid [1][2]. Erythromycin thiocyanate also exhibits antitumor and neuroprotective effect in different fields of research [3][4].
|
-
-
- HY-B0220E
-
|
|
Bacterial
Antibiotic
DNA/RNA Synthesis
|
Infection
Cancer
|
|
Erythromycin A dihydrate is a macrolide antibiotic produced by actinomycete Streptomyces erythreus with a broad spectrum of antimicrobial activity. Erythromycin A dihydrate binds to bacterial 50S ribosomal subunits and inhibits RNA-dependent protein synthesis by blockage of transpeptidation and/or translocation reactions, without affecting synthesis of nucleic acid [1][2]. Erythromycin A dihydrate also exhibits antitumor and neuroprotective effect in different fields of research [3][4].
|
-
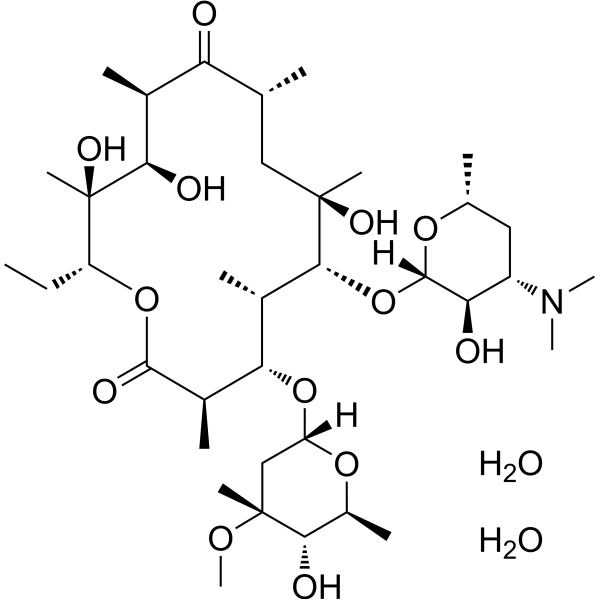
-
- HY-B0220B
-
|
|
Antibiotic
Bacterial
|
Infection
Cancer
|
|
Erythromycin gluceptate is a macrolide antibiotic produced by actinomycete Streptomyces erythreus with a broad spectrum of antimicrobial activity. Erythromycin gluceptate binds to bacterial 50S ribosomal subunits and inhibits RNA-dependent protein synthesis by blockage of transpeptidation and/or translocation reactions, without affecting synthesis of nucleic acid [1][2]. Erythromycin gluceptate also exhibits antitumor and neuroprotective effect in different fields of research [3][4].
|
-
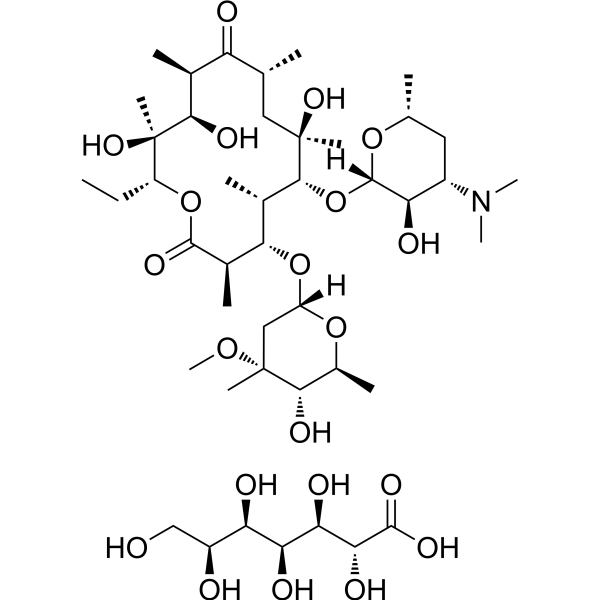
-
- HY-B0220C
-
|
|
Antibiotic
Bacterial
DNA/RNA Synthesis
|
Infection
Cancer
|
|
Erythromycin aspartate is a macrolide antibiotic produced by actinomycete Streptomyces erythreus with a broad spectrum of antimicrobial activity. Erythromycin aspartate binds to bacterial 50S ribosomal subunits and inhibits RNA-dependent protein synthesis by blockage of transpeptidation and/or translocation reactions, without affecting synthesis of nucleic acid [1][2]. Erythromycin aspartate also exhibits antitumor and neuroprotective effect in different fields of research [3][4].
|
-
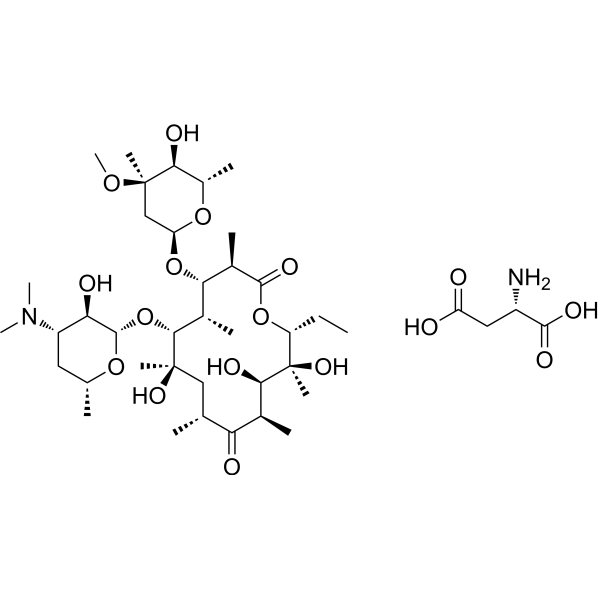
-
- HY-108875
-
|
|
Antibiotic
Bacterial
DNA/RNA Synthesis
|
Infection
Cancer
|
|
Erythromycin stearate is a macrolide antibiotic produced by actinomycete Streptomyces erythreus with a broad spectrum of antimicrobial activity. Erythromycin stearate binds to bacterial 50S ribosomal subunits and inhibits RNA-dependent protein synthesis by blockage of transpeptidation and/or translocation reactions, without affecting synthesis of nucleic acid [1][2]. Erythromycin stearate also exhibits antitumor and neuroprotective effect in different fields of research [3][4].
|
-
-
- HY-B0220A
-
|
|
Antibiotic
Bacterial
DNA/RNA Synthesis
|
Infection
Cancer
|
|
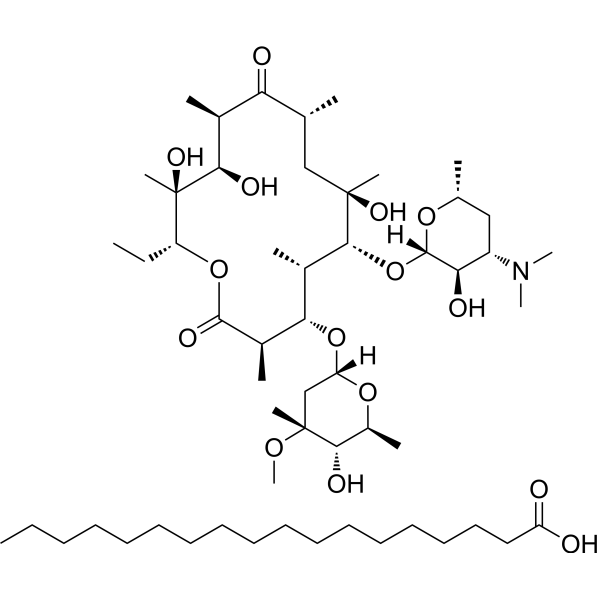
Erythromycin lactobionate is a macrolide antibiotic produced by actinomycete Streptomyces erythreus with a broad spectrum of antimicrobial activity. Erythromycin lactobionate binds to bacterial 50S ribosomal subunits and inhibits RNA-dependent protein synthesis by blockage of transpeptidation and/or translocation reactions, without affecting synthesis of nucleic acid [1][2]. Erythromycin lactobionate also exhibits antitumor and neuroprotective effect in different fields of research [3][4].
|
-
-
- HY-B0509B
-
|
BAY 41-6551 disulfate
|
Bacterial
Antibiotic
|
Infection
Cancer
|
|
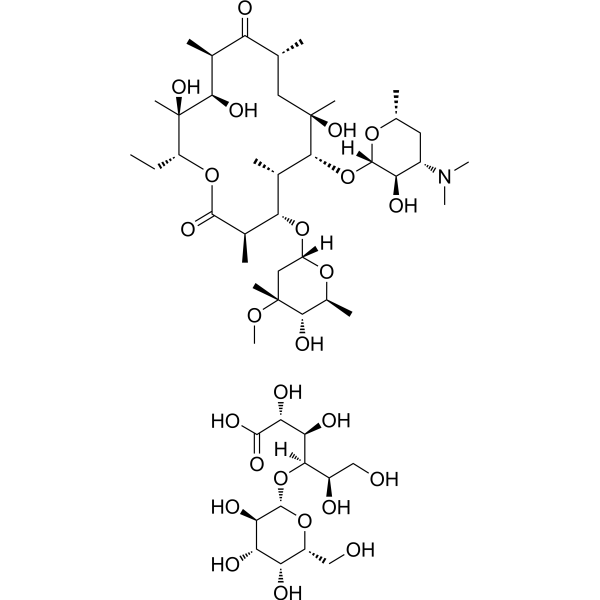
Amikacin disulfate (BAY 41-6551 dissulfate) is an aminoglycoside antibiotic and a semisynthetic analog of kanamycin. Amikacin disulfate is bactericidal, acting directly on the 30S and 50S bacerial ribosomal subunits to inhibit protein synthesis. Amikacin disulfate is very active against most Gram-negative bacteria including gentamicin- and tobramycin-resistant strains. Amikacin disulfate also inhibits the infections caused by susceptible Nocardia and nontuberculous mycobacteria .
|
-
-
- HY-107813
-
|
BAY 41-6551 sulfate
|
Bacterial
Antibiotic
|
Infection
Cancer
|
|
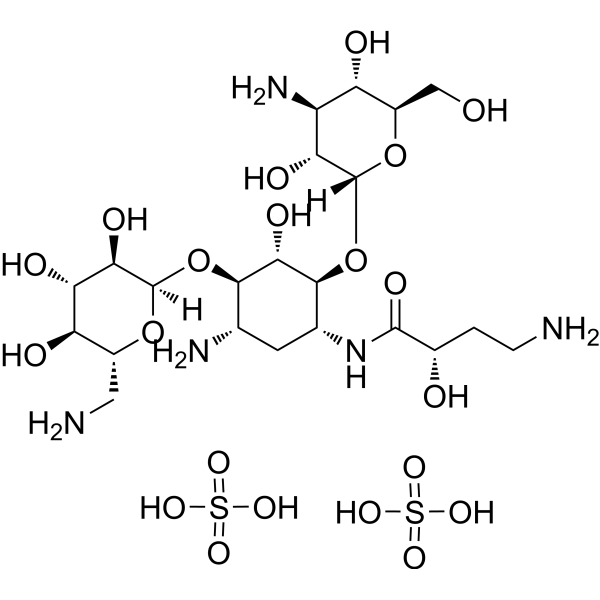
Amikacin sulfate (BAY 41-6551 sulfate) is an aminoglycoside antibiotic and a semisynthetic analog of kanamycin. Amikacin sulfate is bactericidal, acting directly on the 30S and 50S bacerial ribosomal subunits to inhibit protein synthesis. Amikacin sulfate is very active against most Gram-negative bacteria including gentamicin- and tobramycin-resistant strains. Amikacin sulfate also inhibits the infections caused by susceptible Nocardia and nontuberculous mycobacteria .
|
-
-
- HY-N7118
-
|
|
Bacterial
Antibiotic
|
Infection
Cancer
|
|
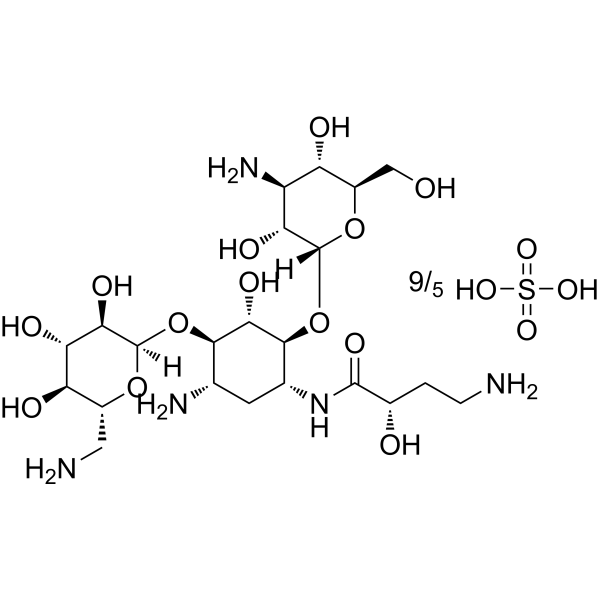
Clindamycin hydrochloride monohydrate is an oral protein synthesis inhibitory agent that has the ability to suppress the expression of virulence factors in Staphylococcus aureus at sub-inhibitory concentrations (sub-MICs). Clindamycin hydrochloride monohydrate resistance results from enzymatic methylation of the antibiotic binding site in the 50S ribosomal subunit (23S rRNA). Clindamycin hydrochloride monohydrate decreases the production of Panton-Valentine leucocidin (PVL), toxic-shock-staphylococcal toxin (TSST-1) or alpha-haemolysin (Hla) .
|
-
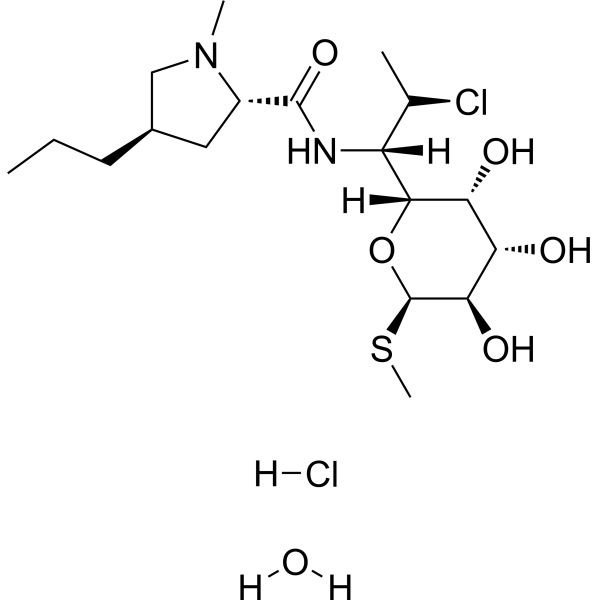
-
- HY-B0220S2
-
|
|
Bacterial
DNA/RNA Synthesis
Antibiotic
|
|
|
Erythromycin-d3 is the deuterium labeled Erythromycin[1]. Erythromycin is a macrolide antibiotic produced by actinomycete Streptomyces erythreus with a broad spectrum of antimicrobial activity. Erythromycin binds to bacterial 50S ribosomal subunits and inhibits RNA-dependent protein synthesis by blockage of transpeptidation and/or translocation reactions, without affecting synthesis of nucleic acid. Erythromycin also exhibits antitumor and neuroprotective effect in different fields of research[2][3][4][5].
|
-
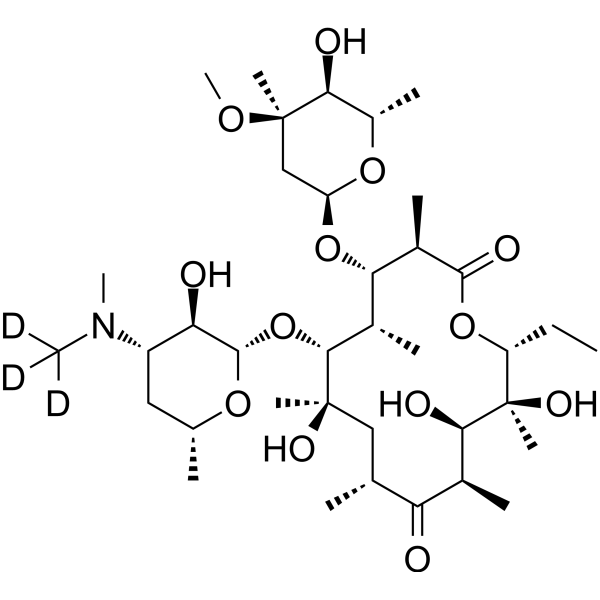
-
- HY-B0220R
-
|
|
Bacterial
Antibiotic
DNA/RNA Synthesis
|
Infection
Cancer
|
|
Erythromycin (Standard) is the analytical standard of Erythromycin. This product is intended for research and analytical applications. Erythromycin is a macrolide antibiotic produced by actinomycete?Streptomyces erythreus?with a broad spectrum of antimicrobial activity. Erythromycin binds to bacterial 50S ribosomal subunits and inhibits?RNA-dependent protein synthesis?by blockage of transpeptidation and/or translocation reactions, without affecting synthesis of nucleic acid [1][2]. Erythromycin also exhibits antitumor and neuroprotective effect in different fields of research [3][4].
|
-
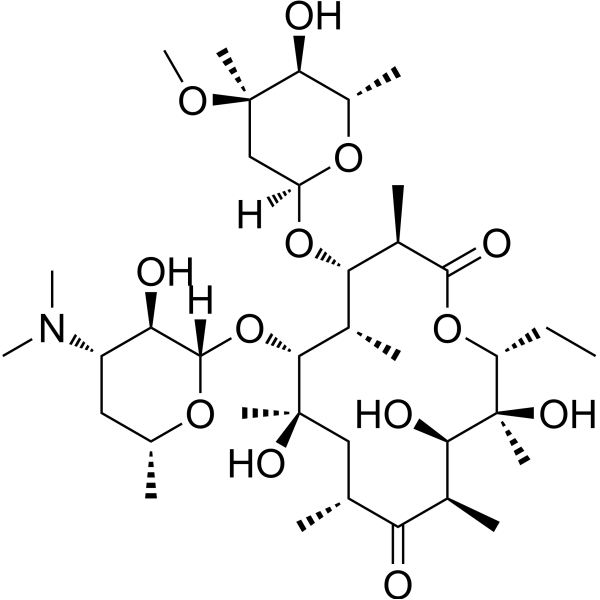
-
- HY-B0479S1
-
|
Thiophenicol-d3-1; Dextrosulphenidol-d3-1
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
|
Infection
|
|
Thiamphenicol-d3-1 (Thiophenicol-d3-1; Dextrosulphenidol-d3-1) is the deuterium-labeled Thiamphenicol (HY-B0479) . Thiamphenicol (Thiophenicol), a methyl-sulfonyl derivative of Chloramphenicol, is a broad-spectrum antimicrobial antibiotic. Thiamphenicol acts by binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit, leading to inhibition of protein synthesis and bacteriostatic effect (against Gram-negative, Gram-positive aerobic and anaerobic bacteria) .
|
-
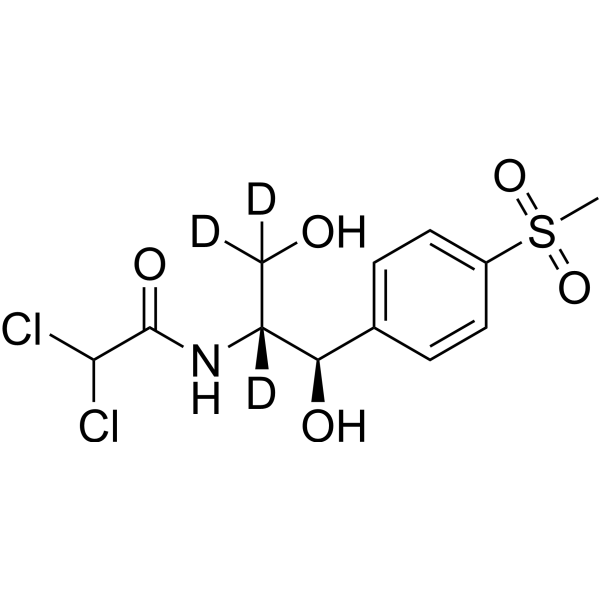
-
- HY-B1455
-
|
|
|
|
|
Clindamycin is an orally active and broad-spectrum bacteriostatic lincosamide antibiotic. Clindamycin can inhibit bacterial protein synthesis, possessing the ability to suppress the expression of virulence factors in Staphylococcus aureus at sub-inhibitory concentrations (sub-MICs). Clindamycin resistance results from enzymatic methylation of the antibiotic binding site in the 50S ribosomal subunit (23S rRNA). Clindamycin decreases the production of Panton-Valentine leucocidin (PVL), toxic-shock-staphylococcal toxin (TSST-1) or alpha-haemolysin (Hla). Clindamycin also can be used for researching malaria .
|
-
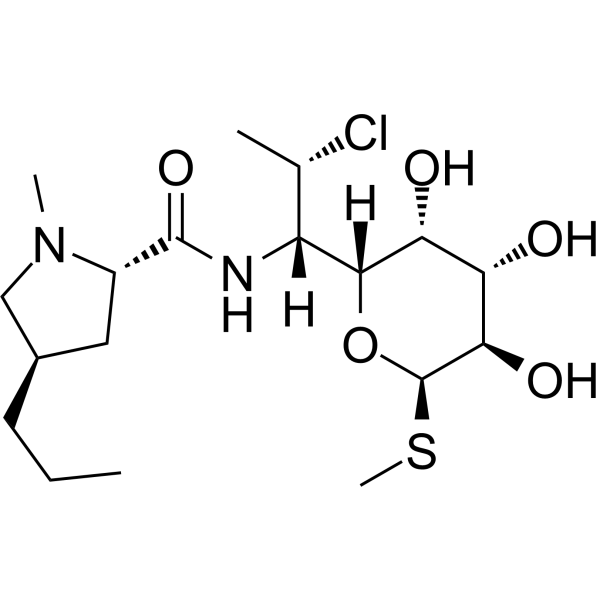
-
- HY-B1455S
-
|
|
Bacterial
Antibiotic
Parasite
|
Infection
|
|
Clindamycin-d3 (hydrochloride) is the deuterium labeled Clindamycin. Clindamycin is an orally active and broad-spectrum bacteriostatic lincosamide antibiotic. Clindamycin can inhibit bacterial protein synthesis, possessing the ability to suppress the expression of virulence factors in Staphylococcus aureus at sub-inhibitory concentrations (sub-MICs). Clindamycin resistance results from enzymatic methylation of the antibiotic binding site in the 50S ribosomal subunit (23S rRNA). Clindamycin decreases the production of Panton-Valentine leucocidin (PVL), toxic-shock-staphylococcal toxin (TSST-1) or alpha-haemolysin (Hla). Clindamycin also can be used for researching malaria[1][2].
|
-
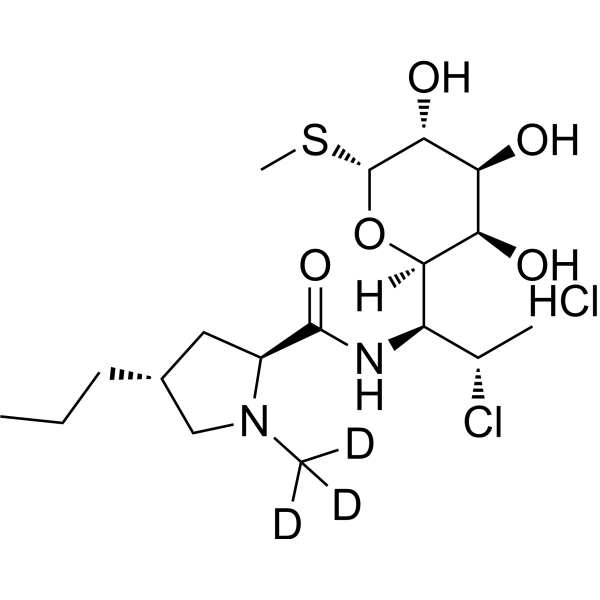
-
- HY-B1455S1
-
|
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
Bacterial
Antibiotic
Parasite
|
Infection
|
|
Clindamycin- 13C,d3 is the 13C- and deuterium labeled Clindamycin. Clindamycin is an orally active and broad-spectrum bacteriostatic lincosamide antibiotic. Clindamycin can inhibit bacterial protein synthesis, possessing the ability to suppress the expression of virulence factors in Staphylococcus aureus at sub-inhibitory concentrations (sub-MICs). Clindamycin resistance results from enzymatic methylation of the antibiotic binding site in the 50S ribosomal subunit (23S rRNA). Clindamycin decreases the production of Panton-Valentine leucocidin (PVL), toxic-shock-staphylococcal toxin (TSST-1) or alpha-haemolysin (Hla). Clindamycin also can be used for researching malaria[1][2][3].
|
-
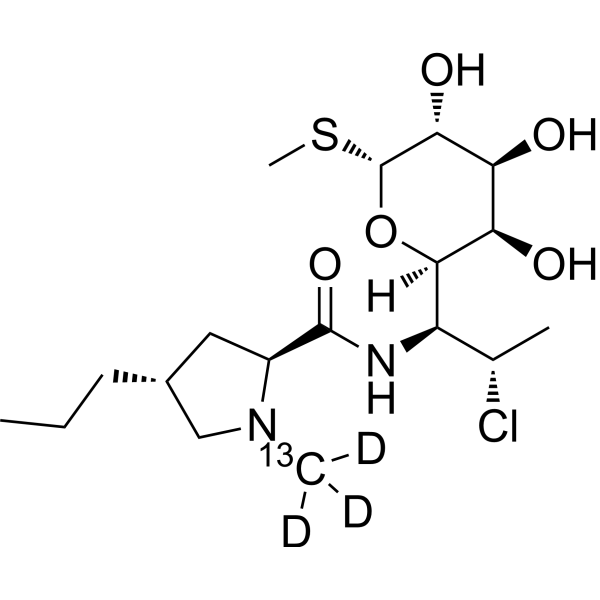
-
- HY-19931
-
COH29
3 Publications Verification
RNR Inhibitor COH29
|
DNA/RNA Synthesis
|
Cancer
|
|
COH29 (RNR Inhibitor COH29) is a potent ribonucleotide reductase (RNR) inhibitor with anticancer activity. COH29 inhibits α and β subunit of RNR with IC50s of 16 μM.
|
-
-
- HY-147352
-
|
|
iGluR
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
NMDA receptor potentiator-1 (Compound 1368) is a subunit selective NMDA receptor potentiator with IC50s of 4 μM and 5 μM against NR2C and NR2D expression, respectively .
|
-
-
- HY-150073
-
|
|
Others
|
Cancer
|
|
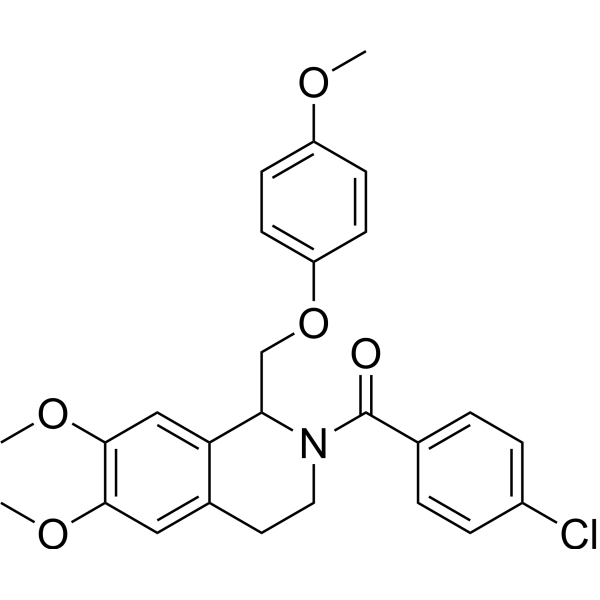
DS01080522 is a Protein Kinase cAMP-Activated Catalytic Subunit Alpha (PRKACA) inhibitor. DS01080522 inhibits PRKACA kinase activity and CREB phosphorylation with IC50s of 0.8 nM and 66 nM, respectively. DS01080522 can be used for the research of cancer .
|
-
-
- HY-149483
-
|
|
nAChR
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
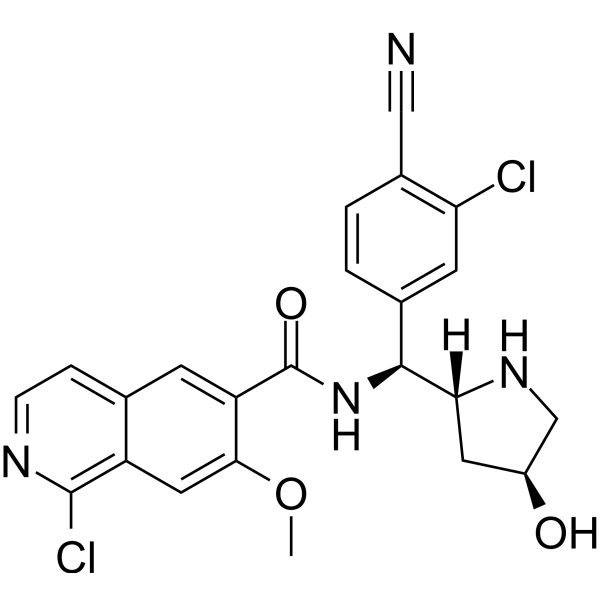
CVN417 is an orally active α6 subunit-containing nAChR antagonist, modulating phasic dopaminergic neurotransmission in an impulse-dependent manner. CVN417 inhibits Ca(2+) effluents mediated by nAChR subunits with IC50s of 0.086 μM (α6), 2.56 μM (α3) and 0.657 μM (α4), respectively. CVN417 attenuates resting tremor in Rodent models, displays the potential to improve movement dysfunction, in conditions such as Parkinson's disease .
|
-
-
- HY-107526
-
|
(Rac)-NFPS
|
GlyT
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
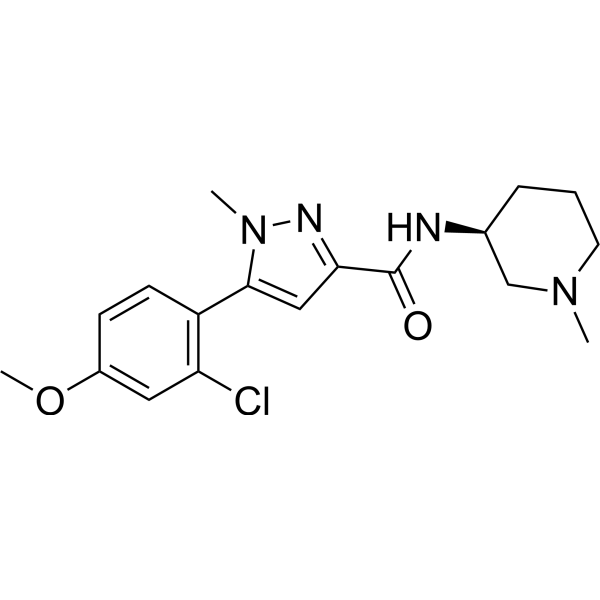
NFPS is a selective, non-competitive glycine transporter-1 (GlyT1) inhibitor with IC50s of 2.8 nM and 9.8 nM for hGlyT1 and rGlyT1, respectively . NFPS exerts neuroprotection via glyR alpha1 subunit in the rat model of transient focal cerebral ischaemia and reperfusion .
|
-
-
- HY-148825
-
-
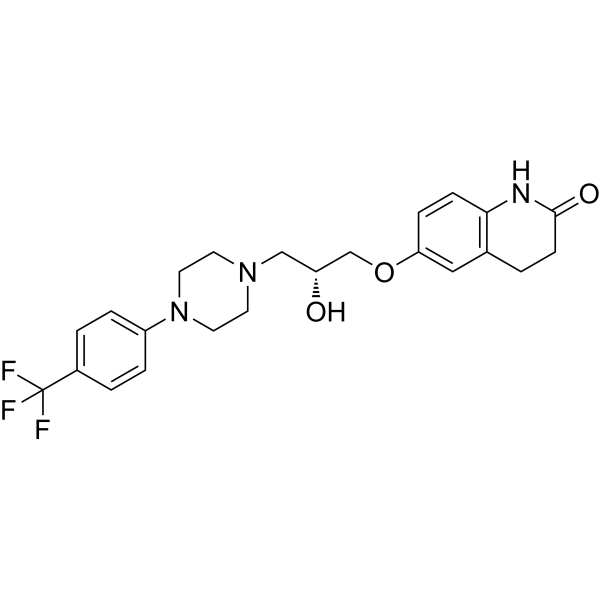
-
- HY-N1074
-
|
Scandenolone
|
Parasite
PKA
|
Infection
Inflammation/Immunology
|
|
Warangalone is an anti-malarial compound which can inhibit the growth of both strains of parasite 3D7 (chloroquine sensitive) and K1 (chloroquine resistant) with IC50s of 4.8 μg/mL and 3.7 μg/mL, respectively. Warangalone can also inhibit cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit (cAK) with an IC50 of 3.5 μM.
|
-
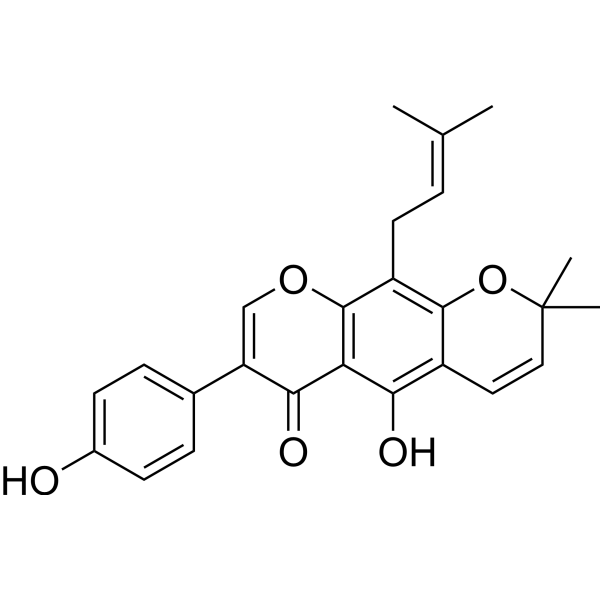
-
- HY-129589
-
|
|
ADC Cytotoxin
|
Cancer
|
|
Thailanstatin A is an ultra-potent inhibitor of eukaryotic RNA splicing (IC50=650 nM). Thailanstatin A exerts effects via non-covalent binding to the SF3b subunit of the U2 snRNA subcomplex of the spliceosome and shows low-nM to sub-nM IC50s against multiple cancer cell lines. Thailanstatin A, a payload for ADCs, is conjugated to the lysines on trastuzumab yielding “linker-less” ADC .
|
-
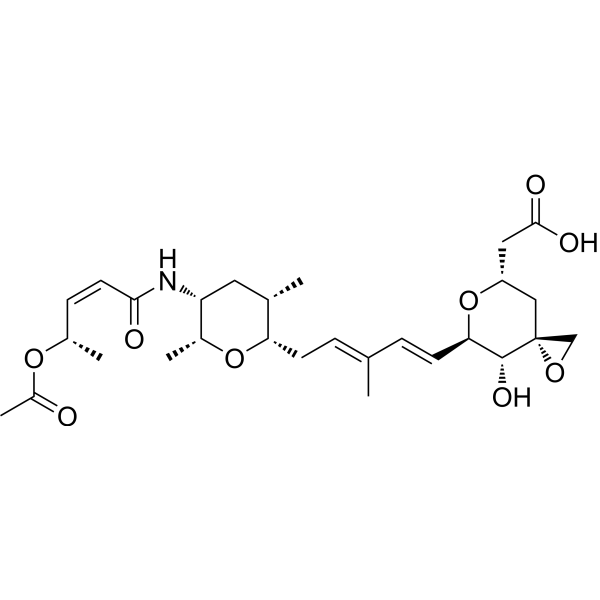
-
- HY-135478
-
|
NCC1048
|
Calcium Channel
Sodium Channel
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
LY393615 (NCC1048) is a novel neuronal Ca 2+ (calcium channel) and Na + channel (sodium channel) blocker with IC50s of 1.9 μΜ and 5.2 μΜ for α1A and α1B calcium channel subunits. LY393615 has good brain penetration and neuroprotective effects in models of in cerebral ischemia that can be used for neurological disease research .
|
-
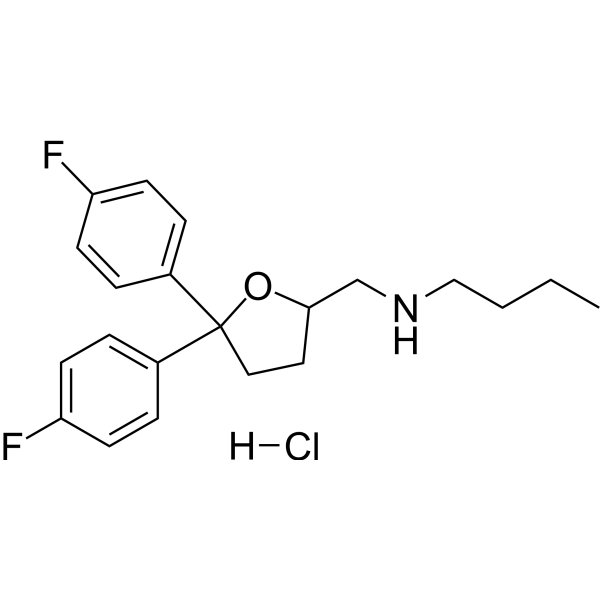
-
- HY-15317
-
RI-1
4 Publications Verification
|
RAD51
|
Cancer
|
|
RI-1 is a RAD51 inhibitor, with IC50s ranging from 5 to 30 μM. RI-1 binds covalently to the surface of RAD51 protein at cysteine 319. RI-1 inactivates RAD51 by directly binding to a protein surface that serves as an interface between protein subunits in RAD51 filaments. RI-1 can disrupt homologous recombination in human cells .
|
-
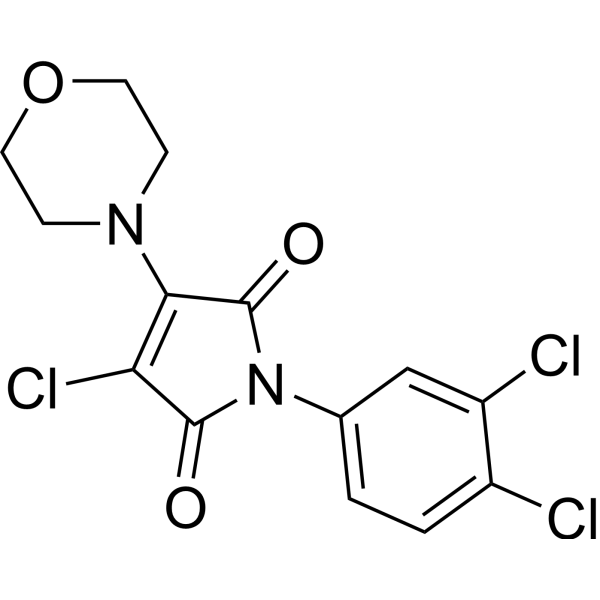
-
- HY-P5149
-
|
αC-PrXA
|
nAChR
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
αC-Conotoxin PrXA is a paralytic peptide neurotoxin and a competitive nAChR antagonist, with IC50s of 1.8 nM (α1β1εδ, adult) and 3.0 nM (α1β1γδ, fetal), respectively. αC-Conotoxin PrXA competes with α-bungarotoxin at the α/δ and α/γ subunit interfaces of the nAChR, shows high specificity against neuromuscular nAChR .
|
-

-
- HY-P5148
-
|
|
nAChR
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
α-Conotoxin BuIA is a paralytic peptide neurotoxin and a competitive nAChR antagonist, with IC50s of 0.258 nM (α6/α3β2), 1.54 nM (α6/α3β4), 5.72 nM (α3β2), respectively. α-Conotoxin BuIA can be used to distinguish nAChRs containing β2- and β4-subunit, respectively. α-Conotoxin BuIA distinguishes among αxβ2 nAChRs with a rank order potency of α6>α3>α2>α4 .
|
-
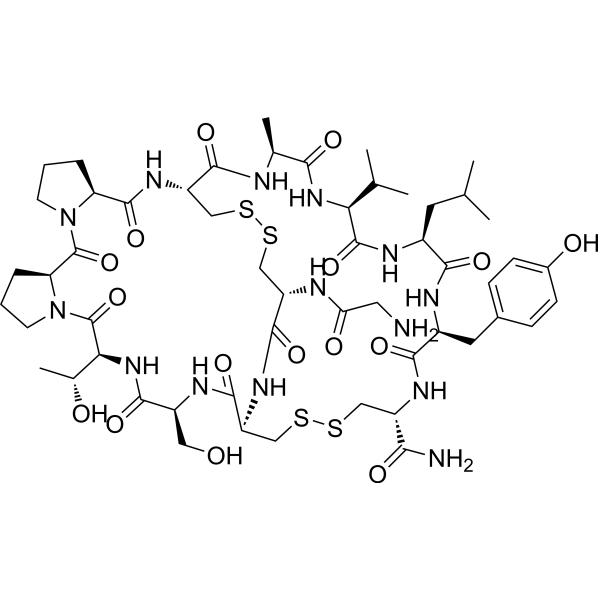
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Target |
Research Area |
-
- HY-P5149
-
|
αC-PrXA
|
nAChR
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
αC-Conotoxin PrXA is a paralytic peptide neurotoxin and a competitive nAChR antagonist, with IC50s of 1.8 nM (α1β1εδ, adult) and 3.0 nM (α1β1γδ, fetal), respectively. αC-Conotoxin PrXA competes with α-bungarotoxin at the α/δ and α/γ subunit interfaces of the nAChR, shows high specificity against neuromuscular nAChR .
|
-
- HY-P5148
-
|
|
nAChR
|
Neurological Disease
|
|
α-Conotoxin BuIA is a paralytic peptide neurotoxin and a competitive nAChR antagonist, with IC50s of 0.258 nM (α6/α3β2), 1.54 nM (α6/α3β4), 5.72 nM (α3β2), respectively. α-Conotoxin BuIA can be used to distinguish nAChRs containing β2- and β4-subunit, respectively. α-Conotoxin BuIA distinguishes among αxβ2 nAChRs with a rank order potency of α6>α3>α2>α4 .
|
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Category |
Target |
Chemical Structure |
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Chemical Structure |
-
- HY-B0479S
-
|
|
|
Thiamphenicol-d3 is a deuterium labeled Thiamphenicol. Thiamphenicol, a methyl-sulfonyl derivative of Chloramphenicol, is a broad-spectrum antimicrobial antibiotic. Thiamphenicol acts by binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit, leading to inhibition of protein synthesis and bacteriostatic effect (against Gram-negative, Gram-positive aerobic and anaerobic bacteria)[1][2].
|
-

-
- HY-B0220S
-
|
|
|
Erythromycin-d6 is the deuterium labeled Erythromycin. Erythromycin is a macrolide antibiotic produced by actinomycete Streptomyces erythreus with a broad spectrum of antimicrobial activity. Erythromycin acts by binding to bacterial 50S ribosomal subunits and inhibits RNA-dependent protein synthesis by blockage of transpeptidation and/or translocation reactions, without affecting synthesis of nucleic acid[1].
|
-

-
- HY-14855S
-
|
|
|
Tedizolid- 13C,d3 is the 13C- and deuterium labeled Tedizolid. Tedizolid (TR 700; Torezolid; DA-7157) is a novel oxazolidinone, acting through inhibition of bacterial protein synthesis by binding to 23S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) of the 50S subunit of the ribosome.
|
-

-
- HY-B0239S3
-
|
|
|
Chloramphenicol-d4 is deuterium labeled Chloramphenicol. Chloramphenicol, a broad-spectrum antibiotic, acts as a potent inhibitor of bacterial protein biosynthesis[1][2]. Chloramphenicol acts primarily on the 50S subunit of bacterial 70S rihosomes and inhibits peptide bond formation by suppressing peptidyl transferase activity[3].
|
-

-
- HY-B0220S1
-
|
|
|
Erythromycin- 13C,d3 is the 13C- and deuterium labeled Erythromycin. Erythromycin is a macrolide antibiotic produced by actinomycete Streptomyces erythreus with a broad spectrum of antimicrobial activity. Erythromycin acts by binding to bacterial 50S ribosomal subunits and inhibits RNA-dependent protein synthesis by blockage of transpeptidation and/or translocation reactions, without affecting synthesis of nucleic acid[1].
|
-

-
- HY-B0220S2
-
|
|
|
Erythromycin-d3 is the deuterium labeled Erythromycin[1]. Erythromycin is a macrolide antibiotic produced by actinomycete Streptomyces erythreus with a broad spectrum of antimicrobial activity. Erythromycin binds to bacterial 50S ribosomal subunits and inhibits RNA-dependent protein synthesis by blockage of transpeptidation and/or translocation reactions, without affecting synthesis of nucleic acid. Erythromycin also exhibits antitumor and neuroprotective effect in different fields of research[2][3][4][5].
|
-

-
- HY-B0479S1
-
|
|
|
Thiamphenicol-d3-1 (Thiophenicol-d3-1; Dextrosulphenidol-d3-1) is the deuterium-labeled Thiamphenicol (HY-B0479) . Thiamphenicol (Thiophenicol), a methyl-sulfonyl derivative of Chloramphenicol, is a broad-spectrum antimicrobial antibiotic. Thiamphenicol acts by binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit, leading to inhibition of protein synthesis and bacteriostatic effect (against Gram-negative, Gram-positive aerobic and anaerobic bacteria) .
|
-

-
- HY-B1455S
-
|
|
|
Clindamycin-d3 (hydrochloride) is the deuterium labeled Clindamycin. Clindamycin is an orally active and broad-spectrum bacteriostatic lincosamide antibiotic. Clindamycin can inhibit bacterial protein synthesis, possessing the ability to suppress the expression of virulence factors in Staphylococcus aureus at sub-inhibitory concentrations (sub-MICs). Clindamycin resistance results from enzymatic methylation of the antibiotic binding site in the 50S ribosomal subunit (23S rRNA). Clindamycin decreases the production of Panton-Valentine leucocidin (PVL), toxic-shock-staphylococcal toxin (TSST-1) or alpha-haemolysin (Hla). Clindamycin also can be used for researching malaria[1][2].
|
-

-
- HY-B1455S1
-
|
|
|
Clindamycin- 13C,d3 is the 13C- and deuterium labeled Clindamycin. Clindamycin is an orally active and broad-spectrum bacteriostatic lincosamide antibiotic. Clindamycin can inhibit bacterial protein synthesis, possessing the ability to suppress the expression of virulence factors in Staphylococcus aureus at sub-inhibitory concentrations (sub-MICs). Clindamycin resistance results from enzymatic methylation of the antibiotic binding site in the 50S ribosomal subunit (23S rRNA). Clindamycin decreases the production of Panton-Valentine leucocidin (PVL), toxic-shock-staphylococcal toxin (TSST-1) or alpha-haemolysin (Hla). Clindamycin also can be used for researching malaria[1][2][3].
|
-

Your information is safe with us. * Required Fields.
Inquiry Information
- Product Name:
- Cat. No.:
- Quantity:
- MCE Japan Authorized Agent:























































